And How Will They Solve Your Business Problems?
by Becky Boyd, MediaFirst PR – Atlanta, http://www.mediafirst.netTuesday, April 1, 2008
By David Abdo, CEO, Bitam
And Walt Kenzie, GM, Bitam US
www.bitam.com
The terminology in the Business Intelligence (BI) space can be quite confusing. There’s BPM, BAM, EPM, and more. What do each of these solutions offer? Which one will solve my business needs? Why choose one over the other?
One definition states, “Business Intelligence refers to technologies, applications, and practices for the collection, integration, analysis, and presentation of business information and also sometimes to the information itself. The purpose of business intelligence is to support better business decision-making.”
BI systems provide historical, current, and predictive views of business operations, most often using data that has been gathered into a data warehouse or a data mart and, at times from operational data. In today’s highly competitive business environment, corporations are generating enormous amounts of data to meet compliance standards, from automation, and from technology solutions like CRM and other. BI systems sort through this data, extract useful information, and turn it into actionable knowledge.
Traditional BI software consists of reporting/trending, query/analysis, on-line analytical processing (OLAP), and data mining. Basically, BI is reporting on data you gathered and generating a report from this data.
Business Performance Management (BPM) and Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) are applications based on BI that give businesses a better picture of how the business is performing, such as historical sales forecast vs. actual. The act of monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time is known as business activity monitoring.
Gartner Inc. defines EPM as, “the methodologies, metrics, processes, and systems used to monitor and manage the business performance of an enterprise.” EPM in short represents the strategic deployment of business intelligence solutions.
EPM, or Enterprise Performance Management, is the next generation of BI that allows companies to take the decisions they made through the BI system and now strategically align these decisions with their corporate goals. Where BI covered the decision process starting at monitoring, then analysis, and finally actions based on key performance indicators (KPIs), EPM aligns or integrates these KPIs into short, medium, or long-term goals. EPM defines the way an organization should operate based on a clear, corporate business strategy containing actions and processes that align to the strategy with identification of KPIs and progress tracking.
EPM involves consolidation of data from various sources, querying, and analysis of the data, and putting the results into practice. EPM enhances processes by creating better feedback loops. Continuous and real-time reviews help to identify and eliminate problems before they grow.
Built on a foundation of BI, EPM marries business intelligence to the planning and control cycle of the enterprise – with enterprise planning, strategic analysis, and modeling or “what-if” capabilities. Fundamentally, EPM is being able to manage the operations of the organization on a holistic scale by managing all the information of the organization, and strategically using this information to meet the business’ mission and vision.
Companies with an EPM system in place can look across the entire organization and know the effect each discipline or business process within the organization has on the other processes of the organization.
How does an EPM system work?
An EPM system looks globally across an organization to gather and consolidate data from numerous sources. The data can be real-time manufacturing data, customer information, operational information, sales, financial data, and more.
It uses key performance indicators, which are financial and non-financial metrics used to quantify objectives to reflect strategic performance of an organization. KPIs are used to assess the present state of the business and to prescribe a course of action. An example of a KPI would be the percent of revenue generated from repeat customers or the value of a sales pipeline.
Modern EPM frameworks utilize KPI sets that provide a measure of both historical and future insights. This provides a reliable assessment of the company’s health and helps drive actions to maximize corporate performance.
Of these frameworks, the most widely known is the Balanced Scorecard, which gives a comprehensive top-down assessment of corporate performance based on the company vision. Beginning with the enterprise vision, managers devise strategies to attain goals consistent with the vision. These strategies are translated into tactical activities, with specific metrics attached to each activity. The metrics serve as the scorecard.
Balanced Scorecards are used to drive strategy execution, clarify strategy and make strategy operational, identify and align strategic initiatives, link budget with strategy, align the organization with strategy, and conduct periodic strategic performance reviews to learn about and improve strategy.
The EPM framework takes into perspective financial, customer, operational, and cultural objectives of the entire enterprise, not just individual business units. This broadens the audience of the system beyond the management team to include departments, employees, customers, shareholders, and more.
What drives a company to use an EPM?
Organizations, large and small, are looking for ways to operate more efficiently, generate revenues, and strategically position themselves for the future. Instead of being reactive in how they manage the business, with EPM systems, companies can become proactive and start making business decisions that will enhance the organization – instead of curing it.
Companies use EPM systems to create and execute business strategies based on reliable information. They use it for their day-to-day operations, strategic planning, long and short, and to generate efficiency within the business processes.
Areas from which top management could gain knowledge by using EPM includes revenues from clients, new customers acquired, repeat buying volume, customer account balances, demographic analysis, profitability of customers by demographic segments, marketing campaign analysis, click through analysis, marketing channel analysis, call center metrics, sales data by product segment, etc.
Every business, both large and small, has macro and micro business issues; macro meaning outside the organization dealing with interactions between vendors, purchasing, and clients. Micros issues relate to how well you are managing the processes within the organization. All of these areas, either inside or outside of the organization, have business processes. With EPM solutions, companies not only uncover ways to better these processes, they uncover problems they didn’t know existed.
Enterprise Performance Management systems maximize corporate performance. They help organizations remain competitive by carefully defining a winning business strategy, integrated with reliable business information, then execute on that strategy. For an EPM to maximize corporate performance, all levels of the corporation need to see and understand how each group is performing relative to their target. Given the amount of data that drives a balanced set of KPIs, and given today’s business velocity, an EPM system must be able to quickly distill massive stores of data into truly actionable information.
What solutions are available in the market? What features should I look for?
There are many different Enterprise Performance Management solutions on the market. Many of these claim to be an EPM, when in fact all they offer is report generation. Businesses need to look for a solution that fits their business needs and does not require them to change their business process to fit the solution. Other key differentiators of a true EPM system include:
1) True integration of data sources within the key EPM areas, from strategic planning to Balanced Scorecard and forecasting, from financial to consolidation, from analytics to reporting. True integration across all areas means you get the real picture of your organization.
2) An EPM solution should fit well into the organization, not forcing the organization to change their business model. The EPM should enhance business processes, making them more powerful, not requiring them to change.
3) The speed in which an EPM solution can be incorporated into the business is another factor for selection. The EPM should integrate within your business quickly with as little a shift of the business as possible.
4) EPM solutions should be a single solution (not one cobbled together from multiple vendors or acquisitions), on a single platform, and allow any authorized person across the organization to access the system. Single solutions like this reduce the total cost of ownership and maintenance within the organization.
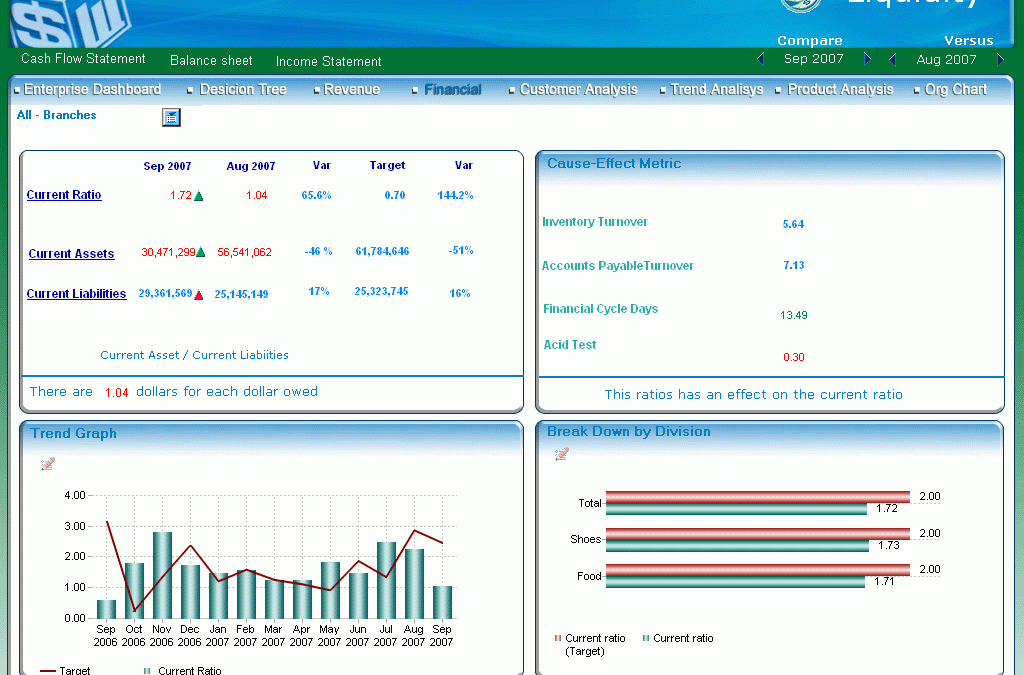
5) Functionality should include: data integration, strategic planning, monitoring, reporting, analysis, dashboards, and scorecarding. Strategy maps create cause and effect relationships between goals and are a great way to visualize what is going on in the organization and how well goals are being met. Dashboards illustrate key performance indicators in a graphical representation such as charts, graphs, tables or maps. The ability to drill down into the dashboard into the underlying detail and perform advanced analysis on those areas allows you to focus on the task at hand, take corrective action, and make well-informed decisions immediately.
Reporting is a fundamental component of any business intelligence infrastructure. Whether an executive needs summary information to manage the business, an inventory manager requires yesterday’s shipping log, or a customer wants account records, reporting the relevant information to the right person in the right format is essential. Some EPM systems offer robust reporting capabilities beyond BI functionality. The ability to post reports through a portal that can be accessed by employees, vendors, or customers allows information to be available to the people who need it, when they need it.
How do I set up an EPM system?
For an EPM to become a useful tool, it is essential that an enterprise understand its goals and objectives and the direction in which the enterprise should progress. Therefore, first define a business plan that articulates the business strategies supported by tactical activities and performance requirements.
Next define metrics and KPIs. These are laid down to assess the present state of the business and to prescribe a course of action. KPI data should be consistent, accurate, timely, and provide an insight into operational aspects and effectiveness of a company.
Third, identify the strategic contribution of every area within the organization. Make sure everyone is on board. BI users can be divided into three major categories: technical users, power users or analysts, and business users. Companies need to choose an EPM solution that is easy to use, no matter what level of technology sophistication the user has. Oftentimes, EPM solutions are so complicated to use that technical users must be called upon to extract reports from the system.
Choose an Enterprise Performance Management technology to implement within your organization.
Map each metric to corporate data. Align each corporate, department, and individual performance to a goal.
Monitor the metrics. Continuously review the process. Adjust tactical activities to keep performance according to plan.
Above all else, make sure executive management has a sense of urgency that they articulate through out the organization to ensure acceptance and success of the new system.
Summary
Corporations are beginning to grasp the benefits that an Enterprise Performance Management system will bring to their business environment – the asset of business intelligence with powerful analysis, monitoring, and reporting – opens the door for stronger competitive presence. Continuous strategic planning and measurement to plan keeps successful companies at the top of their game. Organizations focused on performance can respond quicker to competitive strikes and market changes. Having the right information at the right time gives management the ability to make timely and effective business decisions. Implementing an Enterprise Performance Management solution is a key step towards sustainability and growth.


Recent Comments